Impact of Disruptive Technologies to Employee Engagement
A diverse workforce of all ages, skill sets, cultures and expectations will be operating amid continual change and technology advancement. So how can organization keep people involved, productive and positive along the way?
A really disruptive technology not only alters people's thinking but also their behavior.' - Unknown Over time, firms that invest in digitization outperform their competitors. Such firms are prepared for disruption and are better suited to commercialize new or modern digital channels capable of establishing a larger user base. Clayton M. Chritensen defines disruptive technology as "a new and unexpected technology that can affect existing technologies." (Owuor, 2018).
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain, 3D Printing, Virtual/ Augmented Reality, and the Internet of Things are the five primary disruptive technologies fuelling the global economy and paving the path for the world of tomorrow.
2. These are dubbed disruptive because they outperform existing technologies in terms of performance, price, ubiquity, accessibility, and/or capabilities.
Aside from the benefits of technology, machines replacing human labor has been a continual concern since the beginning of the industrial revolution. (Priyashantha, 2022).
However, these advances may have a detrimental influence on people and their employment since technology improvements, to some extent, replace labor as a factor of production or these developments are beyond the operational understanding of existing personnel. (Sharon & Aggarwal, 2019) Attrition is described in Human Resources as a decline in the workforce as a result of retirement or resignation, with no intentions to replenish or replace that empty employment post. Employee attrition differs from employee turnover in that the vacancies caused by the former process are not replaced immediately, whereas in the latter process, there is a short metric and vacancies must be filled promptly by rehiring. (Owuor, 2018). Employee attrition also has an impact on businesses, which must eventually deal with the loss of labor, which may have been one of their most valuable assets. This research focuses on understanding employee turnover as a result of disruptive technology breakthroughs.
Over the past few years, technology has redefined the connectivity between people, business, consumers and government through the Internet and associated sources. The importance of information technology (IT) in this change cannot be overstated, and it has evolved into the most sophisticated strategic component.
Increasing demand in this industry may be regarded as consumer and corporate demands, as well as economies of scale, which contribute to increased growth in the sector. However, there are still a few occasions where IT services or projects fail owing to bad quality, unfulfilled needs, dissatisfied consumers, financial concerns, and so on. (Priyashantha, 2022). The presence of insufficiently engaged staff in the initiatives is one of the causes for the failure. An engaged employee will demonstrate his or her degree of devotion and interest in the organization and its ideals (Sundaray, 2011).
How Disruptive Technologies are Redefining the Role of Leaders/Managers
Digital transformation is nothing new. Since the dawn of business, organizations have been re-strategizing to capitalize on technological advances.
However, the advent of disruptive technologies, such as virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and predictive analytics, to mention a few, is making digital transformation a prerequisite of doing business for all enterprises. Almost all (94%) of the senior executives polled indicated they have a digital transformation plan in place, and 83% saw themselves as disruptive inside and/or across sectors, with the ability to succeed in a period of continual change. Cloud solutions (59%) are the most often deployed disruptive technology, followed by IoT (51%), AI (45%), and blockchain (31%). [Figure 1]
- Which of the Following technologies are you currently leveraging
The motivations for adopting cutting-edge technology are as diverse, including the potential to innovate (36%), revenue growth (34%), and profitability (32%).
- What are your organization’s top drivers for the adoption of disruptive technologies?
Many firms are able to better execute strategies and adapt to changing market trends and client demands thanks to disruptive technology. However, as our study revealed, a tiny set of firms are leading in this age of disruption. This category, known as top achievers, accounts for 11% of the executives we questioned and includes executives who stated that they:
- Accept a society that encourages perpetual change.
- Understand the need of change management in these times of disruption
- Self-identify as a "disruptor" or "leader" while implementing disruptive, digital, and revolutionary changes.
These high performers are seeing the greatest bottom-line benefits from disruptive technologies \. By analyzing their approaches and strategies to new technologies—which we will outline in this report—we can identify steps other organizations can take to become leaders as well.
To what extent has leveraging disruptive technologies impacted your organization across the following measures?
Disruptive Innovation Theory
Bower and Christensen (1995) pioneered the notion of disruptive innovation theory when they investigated the disk-drive business in 1995. (Christensen et al., 2015; Gobble, 2016; King & Baatartogtokh, 2015; Nagy et al., 2016; Schmidt & Druehl, 2008). Christensen's beliefs are based on the industry's trajectory chart. According to Christensen et al. (2018), during the first interviews with disk-drive managers, the managers addressed the notion resource-allocation procedure, which is known to support sustaining innovation. (Bower, 1970). This means concentrating on new product development with high margins by targeting large markets with well-defined consumers and deprioritizing smaller markets with less well-defined customers. Another hypothesis that evolved was the common resources-dependency theory, which said that firms were dependent on their most vital resources, in this instance consumers (Pfeffer & Salancik, 1978). Furthermore, he built his notion - Disruptive Technologies - by grounding his theory in existing theory. According to the findings of this study, there was a similar pattern in why prominent firms failed as technology and the industry evolved. This tendency was particularly persistent in the disk-industry, where incumbents lost their positions due to technological developments. (Bower & Christensen, 1995). Disruptive innovation theory distinguishes between two types of innovation: sustaining and disruptive. Schmidt and Drugehl (2015) contend that understanding the distinction between these is critical in understanding Christensen's viewpoint. Sustaining is seen to enhance an excellent product for the incumbent's existing customers; these upgrades might be modest or dramatic, but they are always thought to sell 9 more to their most profitable, mainstream client. (Christensen et al., 2015; Christensen & Rosenbloom, 1995). Furthermore, these enhancements frequently correlate to a feature that the majority of consumers value the most, allowing for increased margins and profitability in sales.
Disruptive Technology and HRM
Human capital is the organization's distinguishing force and active asset. (Fitz-enz, 2009). Human capital and business competitive advantage have a favorable and significant link. (Kamukama, 2013). Human resources (HR) are the firm's intangible resources that can provide a competitive advantage because they are difficult for rivals to replicate. (Khandekar and Sharma, 2005). New approaches to human capital management are required to lead and drive growth. (Fitz-enz, 2009).
Being a technology proponent is one of the HR skill areas for human performance and corporate success, which entails enhancing and exploiting technology as well as establishing internal procedures that correspond with external environment expectations. (Ulrich et al., 2011). Electronic human resource management (E-HRM), a concept that uses information technology to execute HR responsibilities, makes it feasible to achieve organizational goals by exerting better control over employee performance and behavior. (Sabir et al., 2015). E-HRM makes the HR function more strategic and effective. Organizations must consider the skillsets of HR professionals in order to make good use of E-HRM.
Employee Innovation
Any company's ability to innovate is critical. According to Premuzic (2015), coordinated group behavior and interpersonal synergy transform creativity into actual invention, the practical aspect of creativity. In the context of service innovation, it may be defined as the re-bundling of diverse resources that might result in the creation of advantageous innovative resources in the context of some actors; this process involves a network of players, which includes the customer.
Kanter (1983) describes innovation as the process of putting any new problem-solving ideas to use, whereas Ven (1986) defines innovation in terms of both the person and the organization. Combining researchers' perspectives on creativity, innovation in the ITindustry may be defined as the use of creative ideas, either new or a combination of existing resources/information, proposed by an individual or small group of individuals in an organization, which when implemented at the appropriate time generates value addition in the product or process for their clients or customers.
Employee Engagement
According to Abraham (2012), employee engagement is the degree to which employees are content with their jobs. Employee job engagement, according to Siddiqi (2015), is about making people attentive and engaged at work in order to achieve a common objective. Work engagement is a separate and distinct concept comprised of cognitive, emotional, and behavioral components related to individual role performance. It has a beneficial affect on employees and increases their interest in their employment. According to Kahn (1990), who examined the physiological influence of personal involvement, physiological engagement and organizational behavior play an important role in cognitive and emotional engagement.
According to the author, engagement happens when employees are intellectually aware and/or emotionally linked with others. Employees who are aware of what is expected of them and who have great relationships with their superiors and colleagues are more likely to be engaged at work. According to Nawaz, Hassan, Hassan, Shukat, and Asadullah (2014), when employees are taught values through empowerment and training, they exhibit engaged behavior. Employees that are engaged are encouraged to be more creative and imaginative in their work. Vance (2006) recognized several components of employee engagement, including excitement for work, long-term commitment, organizational pride, alignment to corporate goals, flexibility, job satisfaction, and so on.
Impact of HR Intelligence
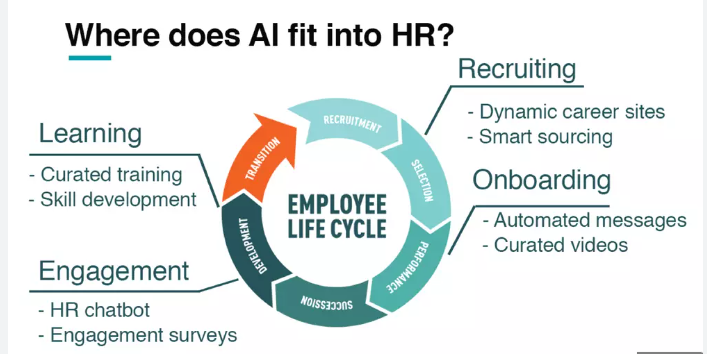
The development of computer systems that accomplish activities that need human intellect is referred to as artificial intelligence. The basic objective of artificial intelligence is to make robots smarter. The Turing test assesses how well AI can impersonate humans. (Evans, 2017). Machine learning is the creation and development of algorithms and techniques that allow computers to learn. This is the method used in artificial intelligence. Google's Allo, Facebook's Messenger, Windows' Cortana, Amazon's Alexa, and Apple's Siri have set the ground for the next wave of key artificial intelligence breakthroughs. (Heater, 2017). They may be accessed via many platforms such as mobile phones, watches, automobiles, home hubs, and so on, and some are multi-platform. (Vincent, 2016). HR executives are experimenting with artificial intelligence across a variety of HR operations like as recruiting, onboarding, development, coaching, and so on.
Impact of Robots
Robots, as defined by NASA, are machines that can perform tasks, and robotics is the study of them. Some robots function autonomously, while others follow human commands. In numerous sectors, robots are employed in a variety of ways. Some robots are made to look like people (humanoid), such as the R2 robonaut, which can think for itself using software, utilize tools, and transmit messages. (NASA website). According to Bernd Schmitt, Professor at Columbia Business School, robots are supercomputers with human-like appearances that pass the Turing test. Previously, robots were solely utilized in industrial systems; now, service robots are now being deployed in organizations. (Bugmann, 2005). Schmitt believes that over the next 20 years, robots will be doing some of the analytical judgments currently performed by human managers, and he advises managers to begin planning for the moment when both human and artificial intelligence will be working together. (Klotz, 2016). The influence of networks HR workers utilize networks for a variety of purposes. Social networks transcend boundaries and come in a variety of forms, including social interactions, multimedia sharing, professional, informative, educational, recreational, and scholarly. Web 4.0 technologies are benefiting practically all key HR activities, and Riemsdijk et al. (2005) listed all of the HR operations that benefit from it, ranging from HR planning through performance management and employee career development, as well as employee relationship management. Recruiters are utilizing social networking sites to assess job applications; LinkedIn provides a resume-like look, while Facebook profiles provide recruiters with a more intimate picture of the individual. (Bohmova and Pavlicek, 2015). Social media is utilized in education and training. (Azeem and Yasmin, 2016). By connecting performance management and learning, organizations promote learning and, in some situations, incorporate learning material into business processes. Current business operations need a new set of skills, competencies, and thought processes from both employees and management (Bersin, 2018), which may be met through learning activities.
Disruptive Technology and HR Practices on Organisational Outcomes
When the internet/intranet is utilized in HRM transactions, the consequences for the organization are grouped into three broad categories: operational (administrative aspects), relational (connection, communication, and collaboration elements), and transformative (strategic aspect). (Panos and Bellou, 2016). Users' acceptance of HR technology fosters a good attitude toward the system while boosting the efficiency of HRM operations and procedures. The acceptability of IT users is required for the achievement of E-HRM goals. (Panos and Bellou, 2016). Sanders (2007) discovered that the usage of e-business technology has an impact on organizational performance both directly and indirectly. E-HRM outcomes include more efficient HRM processes, a higher quality of HR service delivery, strategic contribution of HR, and all of this would result in the achievement of organizational goals (Rul et al., 2007). The use of technology in HR promotes virtual interactions that may be used in areas such as recruiting inside the organization. E-HRM may reduce transactional costs as well as the HR department's head count. Implementing technology in human resource operations improves performance by improving value for users while also conserving people and other resources. (Oladele and Omotayo, 2014). The IT environment has a significant impact on HRM effectiveness since increased utilization results in better value generation. (Sabir et al., 2015). The use of technology in human resources has a favorable impact on HRM responsiveness, service quality, and helpfulness. (Obeidat, 2016)
Employee engagement measurement, tracking, and reporting is reasonable and required, according to Wzorek (2019). Employee engagement closely correlates to productivity, which has an influence on the organization's profitability. Current self-reporting systems, according to Wzorek (2019), are a beginning in the right direction, but as leaders, we must insist for better. Current self-reporting restrictions include:
1. Distraction from core jobs, vital obligations, and responsibilities that add value: Most businesses maintain a consistent cycle of employee-engagement surveys. Daily or weekly pulse surveys, as well as more comprehensive monthly, quarterly, and yearly surveys, are some examples. Employees are overloaded with surveys that take their time and distract from value, creativity, and invention when paired with 360-degree evaluations, vendor, and industry surveys.
2. Lack of honesty in reporting accuracy: Most employee engagement surveys offer anonymity, but employees may not always give honest answers. In their honesty about how happy, content, and protected individuals feel, there are usually minor to major variances. This is a typical and inherent limitation of human data collecting.
3. Disconnect between how employees feel and the work they are doing: Employees may report attitudes that are unrelated to their activities, actions, and behaviors through the system when assessing via self-reporting. Inputs and outputs are measured by project and task management systems. Engagement is measured using survey methods. Two strongly and closely connected processes run blindly independent of each other. This is where I see the most opportunity for significant change.
Tying Employee Activity To Employee Sentiment
According to the human resource council, the intervire conducted by Christine Wzorek with president of White Lable Advisors and Advisory Cloud Members, the discussion elaborate how they are Tying Employee Activity To Employee Sentiment (Wzorek, 2022).
“We need disruptive technology that can help with project/task management and monitor employee engagement in real time…...”. “Most businesses currently use project/task management software as a central center for communication, tracking, and activity. Because employees are generating the deliverable within a platform, it makes reasonable for it to also track their behavior in real time…...”.
“We've all been there and can empathize — working from a cloud-based project management software that overwhelms us with direct and indirect assignments, dependencies, project tracking of other teams, and so on. We've pushed back start dates, stretched timeframes, and skipped tasks, either due to roadblocks, other delayed projects or tasks from a team member or another team, or just because we don't want to perform them over another work or project. Our natural inclinations, knowledge, talents, and abilities influence our actions inside project and task management systems, eventually influencing and enhancing how we give deliverables……”
“With AI developments and data analytics sophistication, it is time to start obtaining employee engagement data through our systems, boosting accuracy in real time. Monthly, quarterly, and annual surveys lag, and we miss out on identifying and adjusting small behavioral changes as they occur, whether in response to a change in frontline, first-tier management; the introduction of a new policy; or the re-commitment and full support of a lightly adhered-to policy…….”
Guidelines for Adopting Disruptive Technology in HRM Practices
According to Owusu-Ansah et al. (2016), in order to improve performance, people's technostress (change and uncertainty caused by the introduction of new technology) must be addressed, since it may have negative implications in the workplace. Organizations must commit time, skill, and resources in order to install new technology or replace older technology. The HR system must be simple to use, and the conditions must aid the installation process. (Sabir et al., 2015). After weighing the advantages and results, the organization must assess its existing position and pick which technology to deploy. The goals and objectives must be determined particularly based on the organization's existing situation and strategy. Finally, integration of the IT and HR departments is required for the proper operation and use of technology in HR (Chaturvedi, 2016).
Change in the Role of HR Manager
HR processes are quickly evolving as a result of changes in business practices brought about by the influence of new technology in this turbulent business climate. (Azeem and Yasmin, 2016). HR practitioners may now perform HR administrative services more effectively thanks to technological advancements. It also plays an important function in engaging with consumers both inside and outside the organization. (Ulrich et al., 2011). HR managers may advocate, access, evaluate, and match technology with HR services for information, efficiency, and connections as technology advocates. (Sharon & Aggarwal, 2019). HR must comprehend and use technology to share information, improve HR operational utility, communicate with people both within and outside the firm, and leverage social media platforms. (Mehra, 2021). According to this blog, HR managers must increase their performance by implementing various types of technology such as AI, robotics, and social networks.
References
1.Arshi, T. & Danamaraju, V. R., 2019. Assessing impact of employee engagement on innovation and the mediating role of readiness for innovation. International Journal of Comparative Management.
2.Insight, F., 2022. TheC-SuiteOutlook:How DisruptiveTechnologiesAre Redefin - Role of Management. p. 16.
3.Mehra, V., 2021. The Impact of Disruptive Technologies on Employee Attrition. International Journal for Research in Engineering Application & Management, Volume 1, p. 12.
4.Owuor, E., 2018. IMPACT OF DISRUPTIVE TECHNOLOGY ON THE PERFORMANCE OF INSURANCE FIRMS IN KENYA. Journal of Strategic Management.
5.Priyashantha, K., 2022. Disruptive technologies for human resource management: a conceptual framework development and research agenda. Journal of Work-Applied Management, 24(6), p. 122.
6.Sharon, D. & Aggarwal, V., 2019. Impact of disruptive technology on human resource management practices. International Journal of Business Continuity and Risk Management .
7.Wzorek, C., 2019. We Need Disruptive Technologies To More Accurately Measure Employee Engagement. 30 Octomber.


Excellent implementation, and I'd want to add the following to your article: disruptive innovations for HRM are seen to be the ones that have the potential to completely alter the HRM landscape. This study focused mostly on the topics covered by an empirical examination between 2000 and 2020. The PRISMA article selection criteria were employed for this review to screen 17 of the 146 total publications retrieved using Scopus and LENS.ORG. The SLR was used as the approach. It is an objective method of reviewing the literature that does not rely on the subjective perceptions of reviewers but rather uses scientific and quantitative methods.
ReplyDeleteWell Done !
Tharanga Jayasundara, thank you for your comment, this article im discussed the importance of disruptive innovations and their importance,
DeleteDisruptive innovation in HR is about the necessity of delivering a new value proposition in the internal corporate market in which HR operates and disrupts the way it provides services to the people and the company. It’s about better serving the internal client and displacing the old ways to operate.
Further Disruptive innovation helps to gain competitive advantages as well as a corporate success, here electronic HRM, and artificial intelligence can be observed under descriptive innovation
Actually, disruptive employee engagement activities go beyond traditional approaches to boost employee morale and productivity. Disrupting usual routine will enhance employee engagement and promote a sense of belonging among employees and contribute more motivation and productive workforce.
ReplyDeleteIresha Udari, thank you for your comment, as you mention disruptive employee engagement became the most popular concept used by well-established organizations to reinforce employee motivation, and morale, which finally leads to high employee productivity,
Deletefurther, it leads to employee ownership of work and autonomy, hence satisfied employees are contributed their maxim output for the company, ultimately which leads to gaining a competitive advantage.
Good work. The impact of disruptive technologies on employee engagement is complex and context-dependent. While these technologies can bring many benefits, organizations must also take steps to mitigate any negative impacts and support their employees through the transition. Well done.
ReplyDeleteA well-studied and maturely written article on the topic. Well done...!!!
ReplyDelete